Risk Adjustment is used in the Medicare and Medicaid programs to adjust capitated payments to ensure equitable reimbursement for delivering healthcare services and benefits to individuals enrolled in healthcare plans.
Medicare is a federal government-funded program that offers
healthcare insurance to people 65 and above to cover their medical
expenditures. In the United States, Medicare is also available for some
impaired people under the age of 65. On the contrary, Medicaid is a huge
federal and state healthcare program covering72.5 million Americans, including
low-income strata such as pregnant females, children, needy families,
pensioners, and disabled people.
The risk adjustment model of the Centers for Medicare &
Medicaid Services (CMS) generates risk scores for Medicare participants by
using the Hierarchical Condition Category (HCC) Coding method. It helps in
predicting future healthcare costs for participants. The risk adjustment
analysis is based on diagnostic information extracted from claims and medical
records gathered by healthcare facilities, inpatient and outpatient visits, and
healthcare services.
The HCC Coding technique categorizes similar medical
conditions based on resource utilization. Higher category risk scores indicate
higher expected healthcare expenditures. Healthcare providers who actively take
part in the risk-adjusted sector of Accountable Care Organizations (ACOs),
Medicare's Hospital Value-Based Program (HVBP), or Medicare Advantage (MA) must
employ accurate HCC Coding and documentation.
M.E.A.T is Necessary for HCC Coding
CMS mandates that documentation in the medical record material
reflect the provider's strategy for patient assistance or Monitoring,
Evaluation, Assessment, Treatment (M.E.A.T) of the disease. The term M.E.A.T.
is crucial for accurate HCC Coding and medical documentation. It is
described as follows:
Monitor: To keep an eye on
signs, symptoms, disease progression, and regression.
Evaluate: To check test
findings, medication efficacy, and treatment outcomes.
Assessment: It includes
consultation, document analysis, and counseling services.
Treatment: This stage comprises
prescription, treatment procedures, and other modalities.
Healthcare organizations must keep in mind that if M.E.A.T. is not
reported to establish a diagnosis, CMS will reject the diagnosis owing to the
lack of evidence provided by the healthcare provider.
Medicare Risk Adjustment HCC Coding
Higher risk scores or Risk Adjustment Factor (RAF) scores
represent patients with severe disease and predicted health costs; while lower
risk scores signify healthier individuals. However, the low-risk scores may
erroneously imply a healthy population when there is inadequate documentation
or insufficient Medicare risk adjustment HCC Coding. In 2020, RAF Medicare
scores will be adjusted based on the patient's HCC condition count.
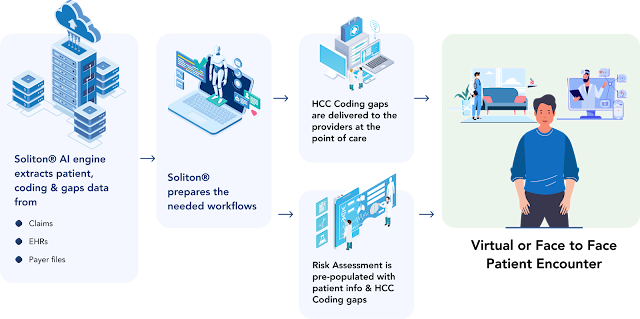
To ease the strain on healthcare providers and coders, healthcare
organizations have started to use CMS Risk Adjustment Solution to
identify and record particular conditions of every patient in their specified
group. The HCC Coding assists CMS in properly and effectively aligning
insurance payments to the resource needs of a Medicare Advantage (MA) group.



No comments:
Post a Comment
Please do not enter any spam link in the comment box