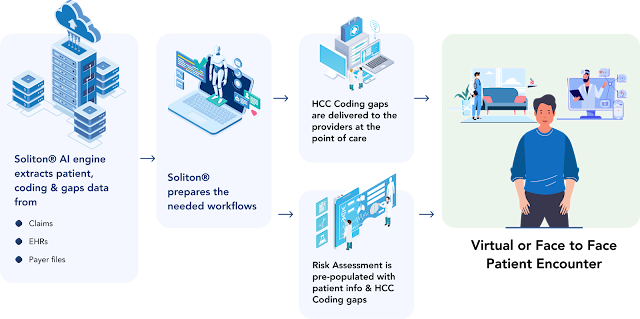
Care Management (CM) is a crucial tool of the Population Health Management Platform. It is a combination of activities aimed at improving patient care and lowering the healthcare cost by boosting care coordination, eliminating redundancy, assisting patients, and clinicians in successfully managing health concerns. These strategies have shown effectiveness for improving quality and controlling healthcare spending for patients with complicated diseases.
Care Management is based on the notion that effective interventions for people within a specific group will lower health risk factors and minimize healthcare costs. It also includes the care coordination initiatives required to assist chronic physical and mental health conditions’ management. An efficient and reliable CareManagement Solution can significantly assist healthcare professionals in achieving the care objectives.
Key Strategies of Care
Management:
There are three primary
strategies to supporting CM for the high-risk group of individuals:
- Identify the
group of individuals whose health risks are manageable.
- Integrate Care Management
services to fulfill the needs of a group of individuals.
- Select,
train, and organize competent staff to provide the specific care services.
Effective care management necessitates coordination and cooperation. Clinicians, caregivers, patients, and healthcare workers must work collaboratively to assist the patient in taking control of their complex medical needs. A comprehensive CM can enable healthcare organizations to decrease expenses while optimizing care quality and efficiency.
Health Plans Supporting
Care Management:
Both the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) and private insurers have started to fund the implementation of CM services by either directly paying for the healthcare services or indirectly paying for the procedures and outcomes leading to successful Care Management.
Patient variables may
benefit from Care Management Solutions, including gender, age, metabolic
parameters, lifestyle factors, chronic condition severity, and some
psychosocial issues – for example, caregiver support, help providers, and health
plans to classify a group of individuals and communities.
Policy ideas that value
practices for attaining the triple aim can assist in the formulation and
execution of Care Management initiatives, and also ensure overall
sustainability. Private health insurers can also provide non-financial
assistance for practitioners’ practice transformation through mentoring,
training collaboratives, and the cooperation of payer-funded Care Management.
Bottom Line:
The Care Management
concept has evolved as a significant practice-based strategy of the Population
Health Management Platform to manage the health of individuals with
complicated or persistent chronic conditions. By merging medical protocols,
research, information technology, support, and guidance, the CM plans can
enhance care quality while helping patients maintain a healthy lifestyle.